Knowledge Distillation 101
source: https://huggingface.co/blog/Kseniase/kd
1. history
- Knowledge Distillation (KD): transfer knowledge from teacher model to a smaller student model
- DeepSeek-R1 proposed effective distillation implementations
- 2006 - Model Compression - Buciluǎ et al
- the first distillation work
- an ensemble of models could be compressed into a single smaller model
- ensemble: a collection of multiple models working together to solve the same problem. their results are combined to a single one
- 2015 - ****Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network - Geoffrey Hinton, Oriol Vinyals, and Jeff Dean
- proposed used the term “distillation”
- instead of training on correct answers, they proposed to give the prob distribution from the teacher model
2. softmax and temperature
- softmax: convert scores (called logits) to probabilities (sum = 1.0)
- temperature (T): control how confident or uncertain a model’s predictions are
- can make the prob distributions more confident (sharp) or more uncertain (soft)
- T = 1 → default softmax: only the correct answer receives 100% prob → hard targets
- T > 1: probs are more spread out or softer → soft targets
- soft targets are useful for distillation. we’ll show why
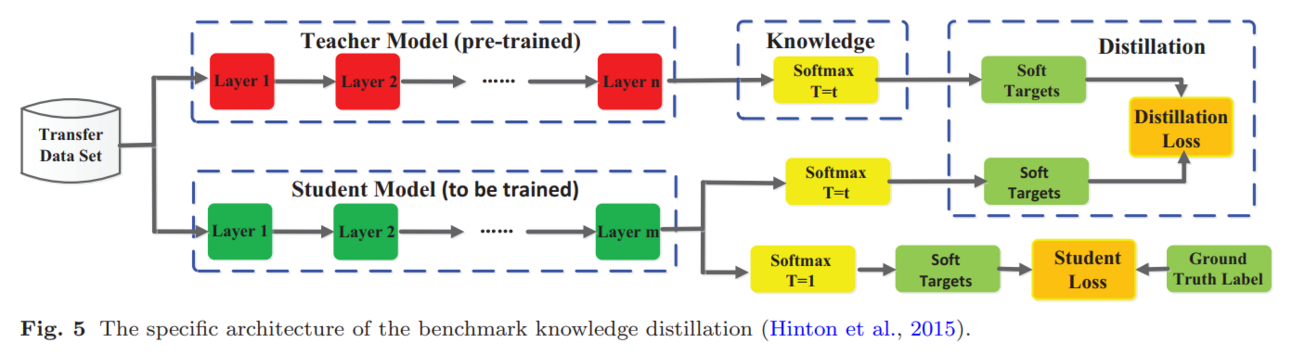
3. distillation steps
- teacher model is trained
- teacher model produces logits
- convert logits to soft targets with T > 1
- student is trained on soft targets (along with hard targets as ground truth)
- goal: minimize the prob distribution difference btw teacher and student
- the student is optimized to mimic the teacher’s behavior (soft targets), not just outputs (hard targets)
- alternative: matching logits instead of probs.
- in high-temperature settings, this method becomes mathematically equivalent to standard distillation
- both approaches lead to similar benefits
4. distillation types
what knowledge can be transfered?
- we have see softmax probs and logits. there are other options
common techniques
https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.05525
Response-based distillation: uses the teacher’s final output probabilities (like above)
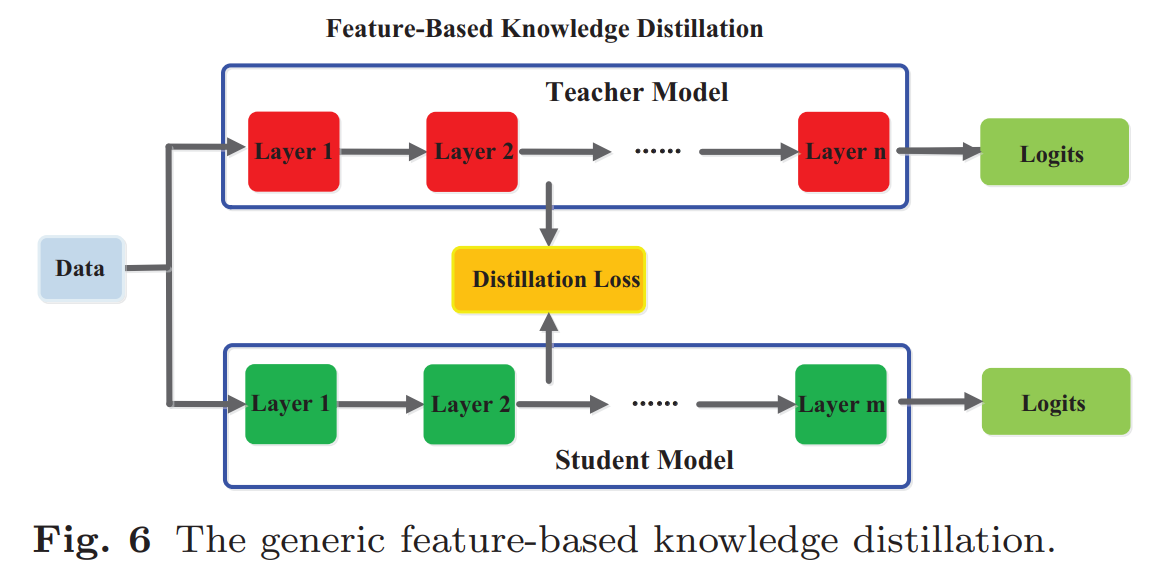
Feature-based distillation: also learns from teacher’s intermediate layers (feature maps)
proposed in https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6550 (2014)
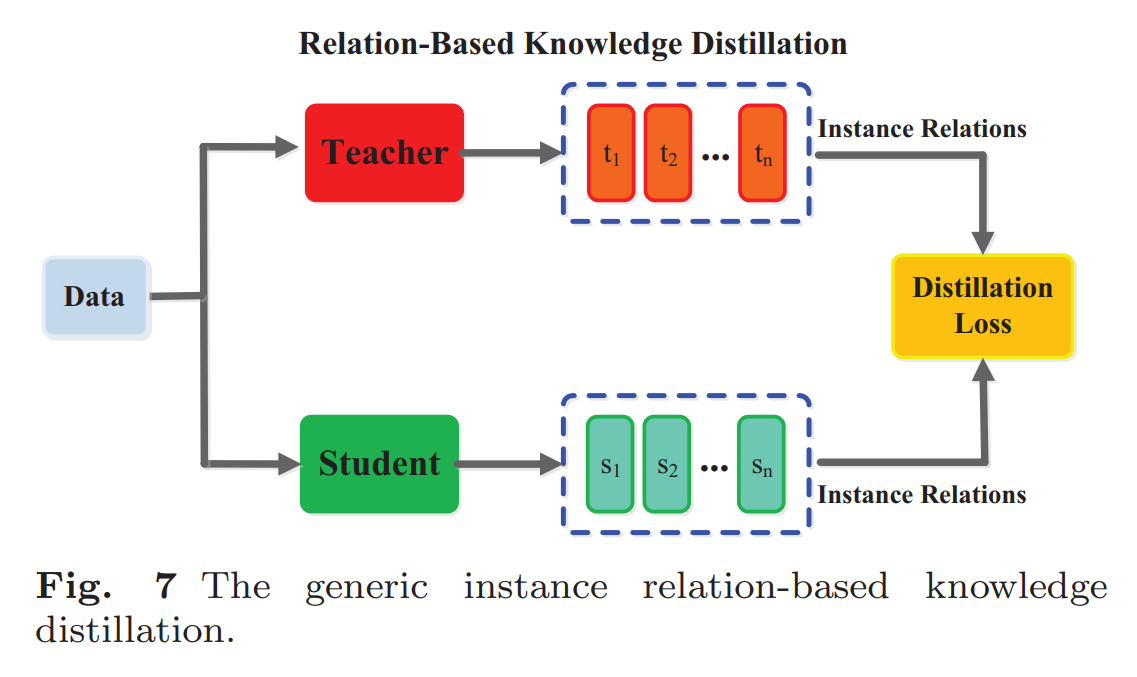
Relation-based distillation: learns relationships btw different parts of the teacher
either between layers or between different data samples
e.g., compare multiple samples and learns their similarities
more complex but can work with multiple teacher models, merging their knowledge
5. training types
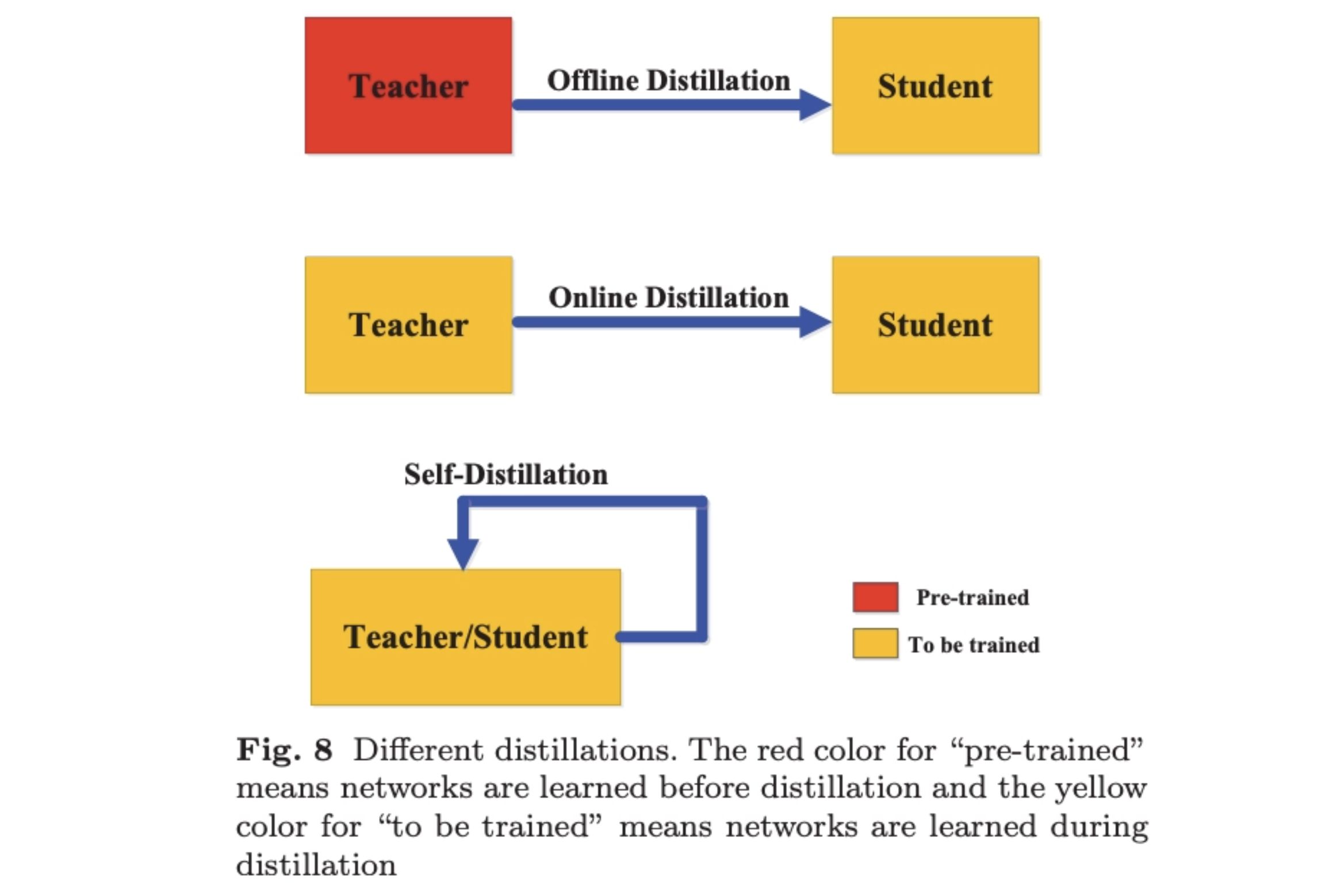
- Offline distillation: teacher is trained first, then teaches student
- Simple, efficient, and reusable teacher
- The student may struggle to reach teacher-level performance due to a knowledge gap
- Online distillation: teacher and student learn together
- Adaptive learning, no need for a separate pre-trained teacher
- Computationally expensive and harder to set up
- Self-distillation: student learns from itself
- The model teaches itself using its own deeper layers
- Might not be as effective as learning from a stronger external teacher
6. improved algorithms
- Multi-teacher distillation: use multiple teachers
- Cross-modal distillation: transfers knowledge btw different modalities (image → text, audio → video, etc.)
- Attention-based distillation: teacher generates attention maps to highlight important areas in the data
- in CV, when identifying a “cat,” the attention map will show bright spots over the ears, eyes, and whiskers (important pixels)
- in NLP, it’s the attention score
- Non-Target Class-Enhanced KD (NTCE-KD): learns incorrect labels as well
- Adversarial distillation: use GAN. generate extra synthetic data. discriminator will check if data is fake or not (compare teacher and student outputs)
- Quantized distillation: apply quantization for student
- Speculative Knowledge Distillation (SKD): student generates draft tokens. teacher selectively replaces low-quality tokens → on-the-fly high-quality training
- Lifelong distillation: Model keeps learning over time
7. distillation scaling laws
We want to predict how effective distillation will be
Apple and the University of Oxford have a good study on this. main findings:
effectiveness is related to, teacher’s size and quality, student’s size, and # training tokens
- power law: performance improves in a predictable way but only to a point
- if student is small, you can use a smaller teacher to save compute
- if student is large, you need a better and larger teacher
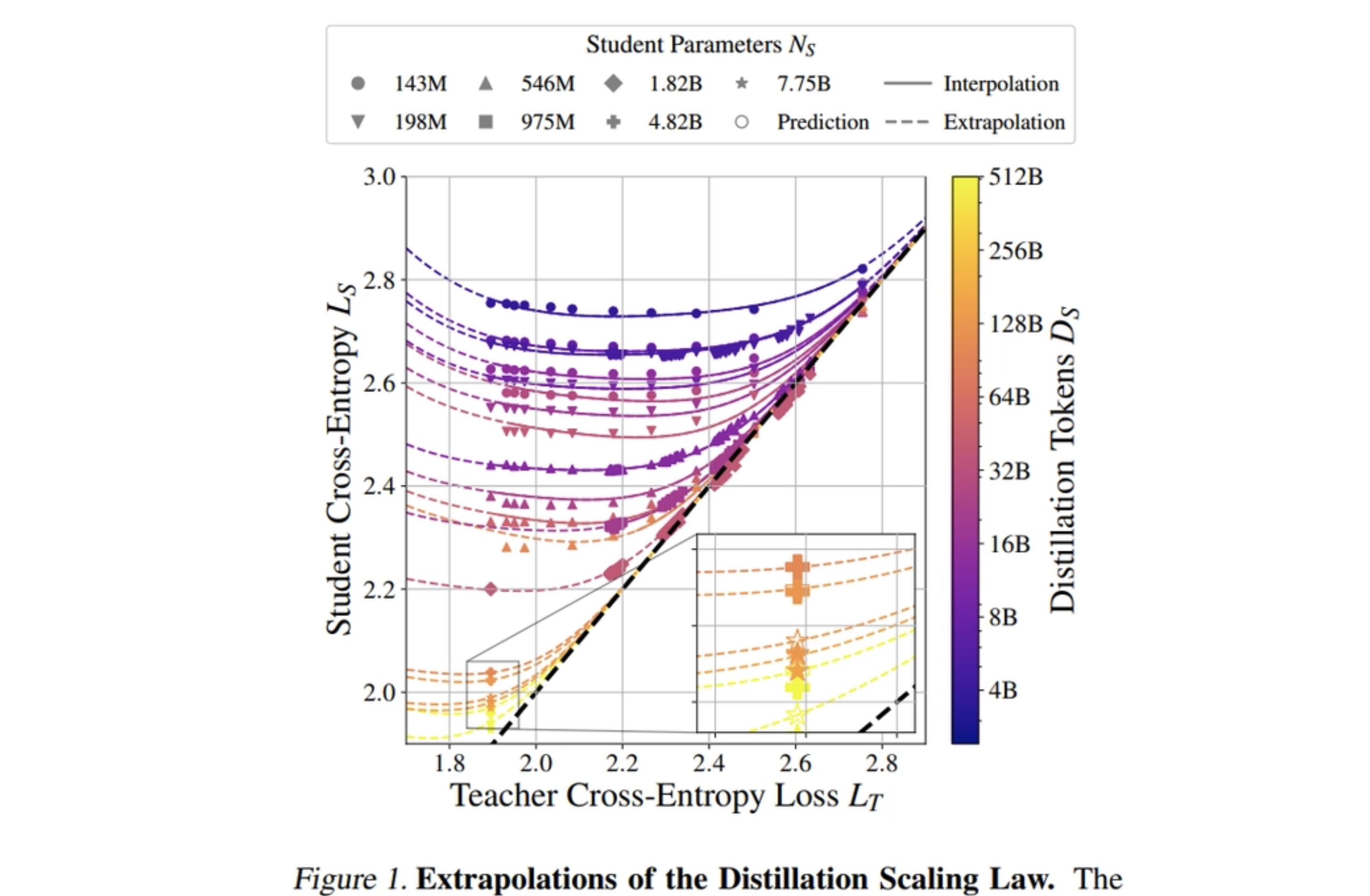
a good teacher doesn’t always mean a better student.
- capacity gap: if teacher is too strong → student might struggle to learn from it
distillation is most efficient when
- student is small enough that traditional supervised training is more expensive
- supervised training only relies on ground truth labels
- when model is small, its capability is less → harder to learn → needs massive training
- teacher already exists, so the cost of training is not required
- student is small enough that traditional supervised training is more expensive
supervised training is more efficient when
- both the teacher and student need to be trained, and teacher training is more costly
- enough compute and data are available
sometimes a student model can even outperform its teacher
8. distill Deepseek-R1
one study finetuned Qwen and Llama using the 800k training examples from DeepSeek-R1
DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B model outperformed QwQ-32B on reasoning benchmarks